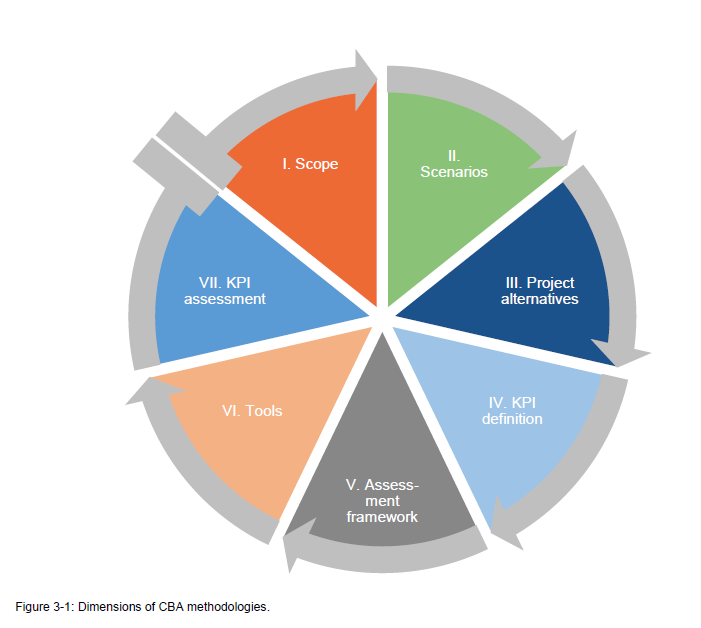
Existing CBA methodologies are mostly insufficient when assessing complex systems, such as meshed offshore grids. Therefore, a suitable CBA methodology needed to be developed within the scope of PROMOTioN, to assess the value of alternative configurations of offshore grids to society. DNV GL, together with Tractebel and TenneT TSO B.V., performed a study within the PROMOTioN project to develop such a methodology. The study delivered a set of guidelines for performing a societal CBA analysis for offshore grids. The methodology presented aims to enable the comparison of alternative offshore grid configurations in a specific geographical area, given developments in offshore wind capacity in the chosen area. The CBA methodology sets out the criteria and guidelines for the assessment of the costs and benefits of a complex project, i.e. an offshore energy system. A common set of indicators (KPIs) is proposed to compare all project alternatives in a transparent manner.
An offshore grid is defined in the context of the CBA methodology as a configuration of offshore infrastructure assets that enables:
- the connection and evacuation of expected offshore wind energy in a defined offshore area to surrounding onshore grids, and
- the increase of market integration through offshore cross-border interconnections.
The societal CBA methodology presented in Deliverable 7.11 provides guidelines on the available choices and options for comparing offshore grid solutions, the KPIs to appraise alternative offshore grid configurations and the assessment framework that will be used for calculating the final CBA. Both an ideal and a pragmatic CBA methodology have been developed. The ideal methodology provides a more accurate reflection of the costs and benefits but will be more time consuming and challenging regarding data collection and the necessary market- and network-based simulations. There is also a risk that a large number of the data points required for the ideal CBA do not exist. The ideal methodology encompasses more complexity and levels of detail. To fit within the scope of the PROMOTioN project, an additional, more pragmatic, CBA methodology has been described in order to enable the assessment within the given scope and time constraints. This pragmatic methodology will be employed within WP 12 to execute the CBA.
